---
title: Branch expiration
subtitle: Learn how to use Neon's branch expiration feature to automatically delete
temporary branches
summary: >-
Covers the setup of Neon's branch expiration feature, enabling automatic
deletion of temporary branches by setting expiration timestamps through the
Console, CLI, or API.
enableTableOfContents: true
updatedOn: '2026-02-06T22:07:32.925Z'
---
## Overview
Branch expiration allows you to set automatic deletion timestamps on branches. When a branch reaches its expiration time, it is automatically deleted.
**Console:** When creating a branch, **Automatically delete branch after** is checked by default with 1 day selected. You can choose 1 hour, 1 day, or 7 days, or uncheck to disable. When updating an existing branch, you can select a custom date and time.
**CLI:** Use `--expires-at` with [RFC 3339 format](#timestamp-format-requirements) (e.g., `2025-07-15T18:02:16Z`). Note: Expiration must be explicitly set; there is no default.
**API:** Use `expires_at` with [RFC 3339 format](#timestamp-format-requirements) (e.g., `2025-07-15T18:02:16Z`). Note: Expiration must be explicitly set; there is no default.
When and why to use branch expiration
How to set expiration timestamps via Console, CLI, and API
How expiration timestamps and TTL intervals work
Restrictions and best practices
Branching with the Neon CLIBranching with the Neon APIManage branchesBranching workflows
## Why use branch expiration?
Branch expiration is ideal for temporary branches that have predictable lifespans:
- **CI/CD environments** - Test branches that should clean up after pipeline completion
- **Feature development** - Time-boxed feature branches with known deadlines
- **Automated testing** - Ephemeral test environments created by scripts
- **AI workflows** - Temporary environments managed without human intervention
Without automatic expiration, these branches accumulate over time, increasing storage costs and project clutter.
Example expiration durations: CI/CD pipelines (2-4 hours), demos (24-48 hours), feature development (1-7 days), long-term testing (30 days).
## How it works
Branch expiration uses a time-to-live (TTL) model. When you set an expiration on a branch, you're defining how long the branch should exist before automatic deletion.
When you set an expiration timestamp on a branch:
1. The system stores both:
- **Expiration timestamp** (`expires_at`) - The scheduled date and time when the branch will be deleted
- **TTL interval** (`ttl_interval_seconds`) - The duration between creation/update and expiration (e.g., 24 hours = 86400 seconds), a read-only value
2. A background process monitors branches and deletes them after their expiration time is reached
3. If you reset a branch from its parent, the TTL countdown restarts using the original interval
Branch deletion is permanent and cannot be recovered. All associated data and compute endpoints are also deleted. Verify expiration times carefully before setting them.
## Setting branch expiration
You can set, update, or remove expiration timestamps through three interfaces:
- **Console** - When creating a branch, **Automatically delete branch after** is checked by default with 1 day selected. You can choose 1 hour, 1 day, or 7 days, or uncheck to disable. When updating an existing branch, you can select a custom date and time.
- **CLI** - Use the `--expires-at` flag when creating or updating a branch with [RFC 3339](#timestamp-format-requirements) format. Note: Expiration must be explicitly set; there is no default.
- **API** - Use the `expires_at` parameter with [RFC 3339](#timestamp-format-requirements) format. Note: Expiration must be explicitly set; there is no default.
See the [Examples](#examples) section below for detailed usage of each method.
## Timestamp format requirements
The `expires_at` parameter must use [RFC 3339](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3339#section-5.6) format with second-level precision:
**Format patterns:**
```
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ (UTC)
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS+HH:MM (Positive UTC offset)
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS-HH:MM (Negative UTC offset)
```
**Valid examples:**
- `2025-07-15T18:02:16Z` (UTC)
- `2025-07-15T18:02:16-05:00` (Eastern Standard Time)
- `2025-07-15T18:02:16+09:00` (Japan Standard Time)
**Requirements:**
- Time zone is required: use either `Z` for UTC or a numeric offset like `+05:00`
- Fractional seconds are optional but only second precision is stored
- Timestamp must be in the future
- Maximum expiration is 30 days from the current time
Common errors include missing timezone (`2025-07-15T18:02:16`), past timestamps, or combining `Z` with offset (`2025-07-15T18:02:16Z-05:00`).
## Restrictions
To maintain system integrity, expiration timestamps cannot be added to:
- **Protected branches** - Cannot expire protected branches or protect branches with expiration
- **Default branches** - Cannot expire default branches or set expiring branches as default
- **Parent branches** - Cannot expire branches that have children or create children from expiring branches
Branch expiration is not supported with these Neon features:
- **Data API**
- **[Legacy Neon Auth](/docs/auth/legacy/overview)** (the new [Neon Auth](/docs/auth/overview) is supported)
When a branch expires and is deleted, all associated compute endpoints are also deleted. Ensure any critical workloads are migrated before expiration.
## Examples
### Creating a branch with expiration
1. Navigate to the **Branches** page in the Console
2. Click **New branch**
3. Enter branch name and select parent branch
4. By default, **Automatically delete branch after** is checked with 1 day selected. You can choose 1 hour, 1 day, or 7 days, or uncheck to disable.
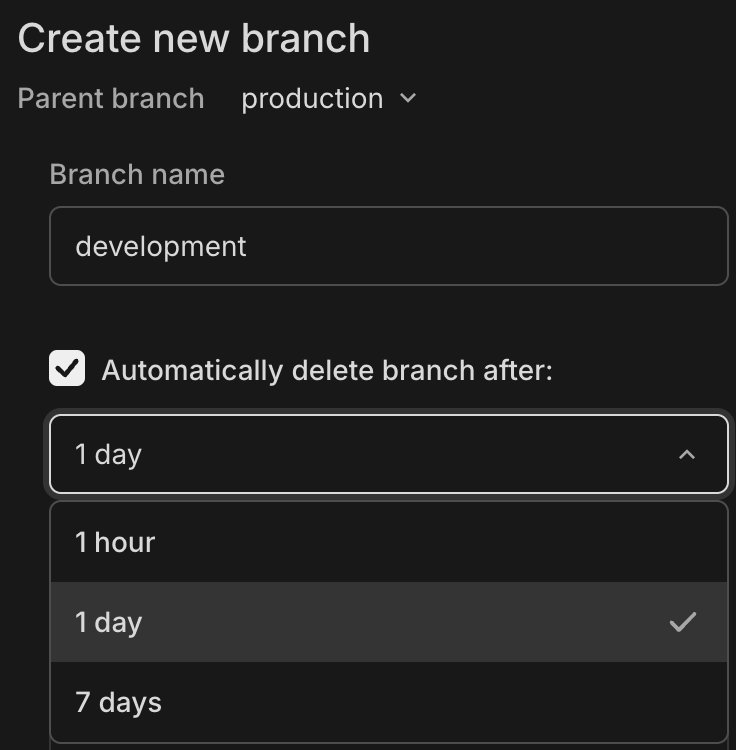
5. Click **Create**
```bash {6,15}
# Create branch expiring at specific date/time
neon branches create \
--project-id \
--name feature-test \
--parent development \
--expires-at "2026-01-29T18:02:16Z"
# Create branch expiring in 2 hours (using dynamic date)
# Linux/GNU: $(date -u -d '+2 hours' +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ)
# macOS/BSD: $(date -u -v+2H +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ)
neon branches create \
--project-id \
--name ci-test \
--parent development \
--expires-at "$(date -u -d '+2 hours' +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ)"
```
```bash {11,21,22}
# Create branch that expires in 24 hours
curl --request POST \
--url https://console.neon.tech/api/v2/projects/{project_id}/branches \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $NEON_API_KEY" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"branch": {
"name": "feature-test",
"parent_id": "br-main-12345",
"expires_at": "2026-01-29T18:02:16Z"
}
}'
# Example response
{
"branch": {
"id": "br-feature-67890",
"name": "feature-test",
"parent_id": "br-main-12345",
"expires_at": "2026-01-29T18:02:16Z",
"ttl_interval_seconds": 86400,
"created_at": "2026-01-28T18:02:16Z"
}
}
```
### Updating branch expiration
1. Navigate to the **Branches** page in the Console
2. Choose the **Update expiration** option for your branch
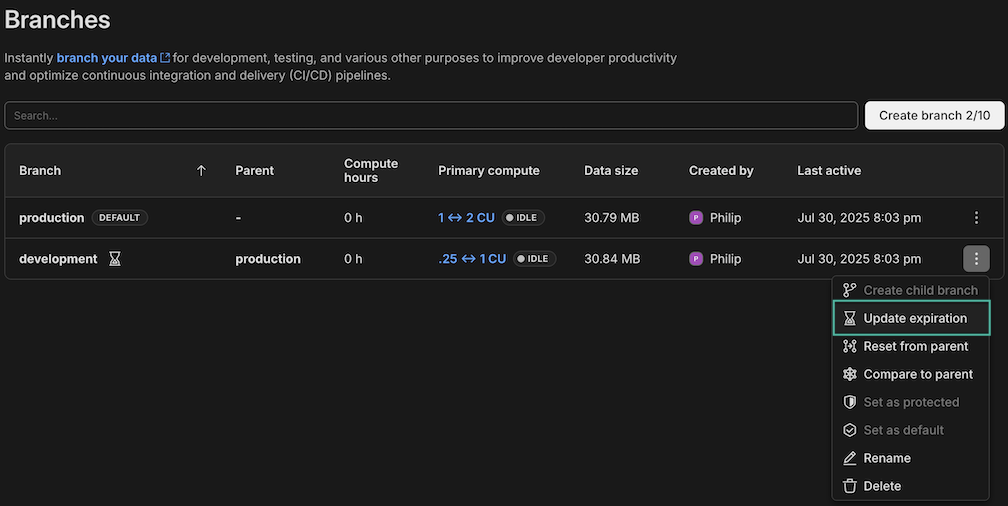
3. To update: Select a new date and time
4. To remove: Uncheck **Automatically delete branch after**
5. Click **Save**
```bash {4,12,18}
# Update expiration to new timestamp
neon branches set-expiration \
\
--expires-at "2026-01-29T12:00:00Z" \
--project-id
# Extend expiration by 7 days from now
# Linux/GNU: $(date -u -d '+7 days' +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ)
# macOS/BSD: $(date -u -v+7d +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ)
neon branches set-expiration \
\
--expires-at "$(date -u -d '+7 days' +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ)" \
--project-id
# Remove expiration from a branch
neon branches set-expiration \
\
--expires-at null \
--project-id
```
```bash {9,21}
# Update branch expiration to specific date
curl --request PATCH \
--url https://console.neon.tech/api/v2/projects/{project_id}/branches/{branch_id} \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $NEON_API_KEY" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"branch": {
"expires_at": "2026-01-29T12:00:00Z"
}
}'
# Remove expiration from a branch
curl --request PATCH \
--url https://console.neon.tech/api/v2/projects/{project_id}/branches/{branch_id} \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $NEON_API_KEY" \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"branch": {
"expires_at": null
}
}'
```
### Retrieving branch information
Check expiration status of your branches:
1. Navigate to the **Branches** page in the Console
2. Click on the desired branch to open the **Branch Overview**
3. See information similar to the following if branch expiration is set:
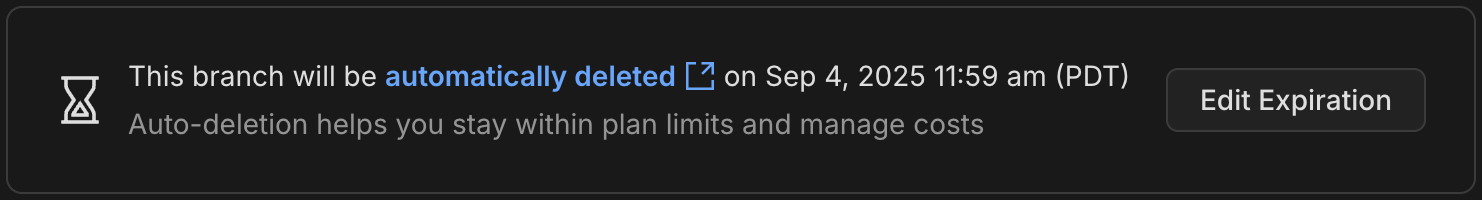
```bash
neon branches info --project-id
```
```bash
curl --request GET \
--url https://console.neon.tech/api/v2/projects/{project_id}/branches/{branch_id} \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $NEON_API_KEY"
```
## API reference
### Create project branch
[`POST /projects/{project_id}/branches`](https://api-docs.neon.tech/reference/createprojectbranch)
- **`expires_at`** (optional) - Timestamp for automatic deletion in [RFC 3339](#timestamp-format-requirements) format
### Update project branch
[`PATCH /projects/{project_id}/branches/{branch_id}`](https://api-docs.neon.tech/reference/updateprojectbranch)
- **`expires_at`** (optional, nullable) - Update or remove expiration
- Timestamp value: Sets/updates expiration
- `null`: Removes expiration
- Omitted: No change
### Response fields
Branches with expiration include two key fields:
- **`expires_at`** - The scheduled deletion timestamp ([RFC 3339](#timestamp-format-requirements) format)
- **`ttl_interval_seconds`** - The original TTL duration in seconds (read-only)
#### How these fields work together
When you create a branch with a TTL of 24 hours, `ttl_interval_seconds` is set to 86400 (seconds). The `expires_at` value is calculated as creation time plus 24 hours.
If you reset the branch from its parent, the `expires_at` value is recalculated using the preserved `ttl_interval_seconds` value, starting from the reset time. The interval itself remains unchanged.
**Example response:**
```json {4,5}
{
"branch": {
"id": "br-feature-67890",
"expires_at": "2026-01-29T18:02:16Z",
"ttl_interval_seconds": 86400,
"created_at": "2026-01-28T18:02:16Z"
}
}
```
In this example, the branch will be deleted 24 hours after creation.